Personality is the unique combination of patterns that influence a human’s behaviour, thought, motivation, and emotion. It is displayed in more than just behaviour and is composed of physical, mental, and social qualities. It is unique to each individual, composed of persistent qualities that exhibit themselves in the form of social behaviour, and is determined by factors such as environment, physical features, and situational factors.
{tocify} {$title=Table of Contents}
Definition
“Personality is the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his characteristics behaviour and thought” – Allport
Roger believed that a person’s behaviour is a factor motivated by self-actualisation tendencies to work and achieve the highest level of their potential and achievement.
Robbins has defined personality as the sum total of ways in which an individual reacts and interacts with others.
Watson. “personality is the sum of activities that can be discovered by actual observations over a long enough period of time to give reliable information”
R. S. Woodworth. “Personality is the quality of the individual’s total behaviour.”
R. B. Cattel. “Personality is that which permits a prediction of what a person will do in a given situation.”
Eysenk. “Personality is the more or less stable and enduring organisation of a person’s character, temperament, intellect and physique, which determine his unique adjustment to the environment.”
In organizational behaviour the study of personality is important because it helps employees modify their behaviour at work, play to their strengths, improve on weaknesses, and interact with coworkers more effectively. This can finally lead to career success and help organizations achieve their goals.
10 Personality Features
Here are various factors that help personality can help us gain a better understanding of ourselves and others. Let’s look at the top 10 personality features:
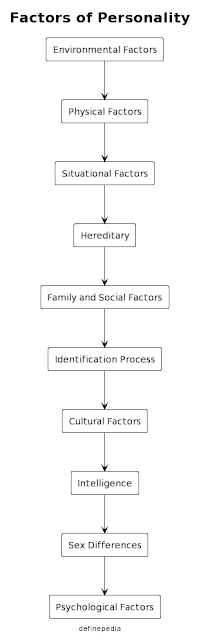
External factors and conditions that shape our personalities, Based on our culture, the people we interact with, and the experiences we have, are examples of environmental variables.
Physical factors include elements of our physical looks and biological elements that might affect our personalities, such as height, weight, and physical health.
Situational factors are the precise circumstances and contexts in which we find ourselves that can influence how we behave and respond.
Hereditary: Because certain features can be passed down through our DNA, our genetic makeup can have a substantial impact on our personality.
Family and social affect: Our familial environment and social interactions can have a huge impact on our personality since we learn certain behaviours and values from those around us.
Identification process: This refers to the way in which we identify with certain people, groups, or cultural norms, which can shape our personality and behaviour.
Cultural factors: Our cultural background can shape our personality in a number of ways, including our values, beliefs, and attitudes towards certain behaviours.
Intelligence has an impact on our personality because it determines how we process information and how we interact with the world.
Sex differences: Because men and women display different patterns of behaviour and have varied social experiences, gender can play a part in developing our personalities.
Psychological factors include a variety of psychological processes and states that might influence our personalities, such as emotions, motives, and mental health.
Characteristics of Personality
Big 5 Personality traits
Personality psychologists agree there are five basic dimensions of personality, often referred to as the “Big 5” personality traits: openness to experience (or extroversion), life satisfaction, open-mindedness, conscientiousness, and neuroticism.
Each trait represents a range between two extremes and researchers support the belief that these five traits are the core of personality. Openness emphasizes imagination and insight, and conscientiousness is defined by the thoughtfulness and goal-directed behaviours. Extraversion is characterized by excitability and sociability. Agreeableness includes traits such as trust and altruism, and neuroticism involves sadness and emotional instability.
Positive personality traits include adaptability, ambition, consideration, and friendliness, while negative traits include manipulation, worrying, and lack of empathy.
Personality traits are thought to be universal and are believed to have biological origins. Research suggests that both biological and environmental influences play a role in shaping our personalities. Twin studies suggest that both nature and nurture play a role in the development of each of the five primary personality traits.
Positive personality traits are those that are beneficial, whereas negative personality traits are more harmful. Factors such as maturation may have an impact on the five personality traits. The situation that someone finds themselves in plays a role in how they might react, although most behaviours are consistent with underlying personality traits.
Big Five, which sounds more like a burger joint than a psychological concept, but I assure you, it’s the real deal.
So, there are five major personality traits that psychologists use to describe how people think, feel, and act.
Openness to experience
First up, we’ve got Openness to experience. This trait covers things like being curious, imaginative, and open-minded. If you’re the kind of person who loves trying new things and exploring different ideas, you might be high in Openness.
Conscientiousness
Next, we have Conscientiousness. This one is all about being responsible, organized, and goal-oriented. If you’re the type of person who always meets deadlines, makes to-do lists, and takes charge of projects, you’re probably pretty high in Conscientiousness.
Extraversion
Moving on, we’ve got Extraversion. This trait is all about being outgoing, sociable, and energetic. If you’re the life of the party, always surrounded by friends and buzzing with energy, you’re likely high in Extraversion.
Agreeableness
Then, there’s Agreeableness. This trait is all about being friendly, cooperative, and compassionate. If you’re the kind of person who’s always willing to lend a helping hand, put others first, and avoid conflict, you’re probably high in Agreeableness.
Neuroticism
Finally, there’s Neuroticism. This trait covers things like anxiety, moodiness, and emotional instability. If you’re the type of person who worries a lot, feels easily stressed, and is prone to mood swings, you might be high in Neuroticism.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is an introspective self-report questionnaire use to identify a person’s psychological preferences in how they perceive the world and make decisions. It is one of the world’s most popular personality tools.
Extraversion and Introversion
Extraversion and Introversion refer to how you direct your energy. Extraverts tend to focus their energy outward, In the other side, Introverts tend to focus their energy inward. It’s important to note that Introversion doesn’t necessarily mean shyness or being a hermit, it just means that you recharge by spending time alone.
Sensing and Intuition
Sensing and Intuition refer to how you gather and process information. Sensors like to focus on the concrete details they can see, hear, and touch, while Intuitives tend to look for patterns and meaning in the information they gather.
Thinking and Feeling
Thinking and Feeling refer to how you make decisions. Thinkers tend to rely on logic and objectivity, while Feelers rely on empathy and subjectivity.
Judging and Perceiving
Judging and Perceiving refer to how you approach the outside world. Judgers like to plan and be organise, while Perceivers like to keep things open-end and be flexible.
Overall, the MBTI can be a great tool for self-discovery and understanding. It can assist you in identifying your own skills and weaknesses, as well as developing new ways to communicate and connect with others.
Criticisms of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) validity include its dichotomous nature, translation of continuous scale scores into nominal categories of preference, and whether it reflects the theory on which it is based. Additionally, many critics cite its poor predictive value.
The test has also been criticized for providing inconsistent and inaccurate results and for having a vast difference between the MBTI theory and what social and personality research suggests. Despite these criticisms, the company has done its own research to refine the test and assess its validity.
Dark Triad
The Dark Triad is a collection of three negative personality traits which are Narcissism, Machiavellianism, and Psychopathy. These traits are not represented in the five-factor model of personality traits, also known as the Big 5. Individuals who exhibit traits of the Dark Triad are often manipulative and exploitative in their interpersonal relationships.
Narcissistic/selfish
An excessive feeling of self-importance, a desire for admiration, and a lack of sympathy for others describe narcissism. A narcissistic person may excessively praise themselves, seek out attention and admiration, and disregard the feelings and needs of others. A person who frequently brags about their achievements and defames others for not being as successful as them, it may show narcissistic tendencies.
Machiavellianism
Machiavellianism is a personality trait that emphasizes manipulation and exploitation to achieve one’s goals. So a Machiavellian person may use deceit and cunning to manipulate others, often without regard for their feelings or well-being. For example, a person who lies, cheats and uses others to advance their own agenda may exhibit traits of Machiavellianism.
Psychopathy
Psychopathy is characterized by a lack of empathy, impulsivity, and a propensity towards anti-social behaviour. A psychopathic person may engage in behaviours that are harmful to others without feeling remorse or guilt. For example, a person who habitually engages in criminal activities lies without hesitation and lacks empathy for others may exhibit traits of psychopathy.
It’s important to note that not all individuals who exhibit traits of the Dark Triad are harmful or dangerous. These traits exist on a spectrum, and some individuals may only exhibit low levels of these traits without causing harm to others. However, it’s important to recognize these traits and be cautious in your interactions with individuals who exhibit them at higher levels.
Was this helpful?
0 / 0