Leasing is a contract between a lessor and a lessee for the hire of a specific asset for a specific period by payment of specified rentals. The maximum period of lease according to law is for 99 years.
Previously land or real estate, mines and quarries were taken on lease. But now a day’s plant and equipment, electronic equipment, civil aircraft and ships are taken on lease.
Definition
A lease is a contract between two parties where one party agrees to rent an asset, such as property or equipment, owned by another party for a specified period and at a specified rate.
There are many leasing companies, such as 1st Leasing Company, and 20th Century Leasing Company.
The different types of leases are discussed below: financial lease, operating lease, sale and lease back leasing, sales aid leasing, specialized service leasing, small-ticket and big-ticket leases, cross-border leasing, and merits and demerits of leasing.
Features of Lease
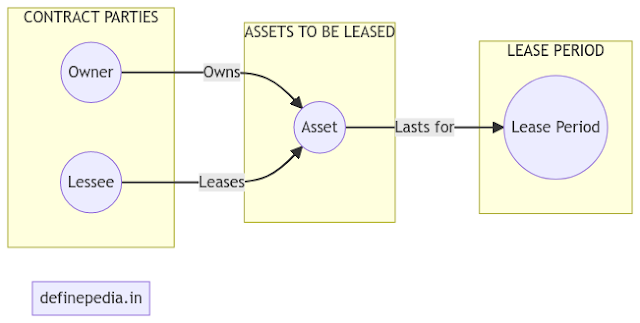
The contract should include details about the parties involved. Such as their names and contact information. It should also specify what assets or properties are being leased, including any relevant details about their condition or location. Finally, it should outline the lease period, including start and end dates.
Two parties
First of all, a lease agreement involves two parties. One is the lessor (or owner of the asset) and the one is the lessee (or user of the asset). Basically, the contract outlines the terms and conditions under which the lessee can use the asset. As well as the responsibilities of both parties during the lease term.
Assets or Property
Another feature of a lease agreement is the assets or property being leased. This could be anything from a commercial property to a piece of equipment, but it must be clearly identified and described in the contract. This ensures that both parties understand exactly what is being leased and what condition it is in.
Lease Agreement
Finally, the lease period is a critical aspect of any lease agreement. This refers to the duration of time during which the lessee can use the asset. A lease may be non-cancelable in some circumstances. It means that the lessee is required to pay for the entire lease term. Other leases may be cancelable, allowing the lessee to terminate the agreement early. But potentially incurring penalties or fees.
You must understand the aspects of a lease agreement, whether you are a landlord or a business owner, to ensure a fair and mutually beneficial relationship. By carefully considering the contract parties, assets or property being leased, and lease period. You can help to ensure a successful lease agreement.
Types of Lease
Basically, there are a few types of lease including financial lease, operating lease, sale and lease-back, sales aid lease, and specialized service lease. Financial leases are used in connection with long-term assets and amortize over the life of the asset.
Operating leases are short-term leases used to finance assets and are not fully amortized over the life of the asset. Sale and lease-back arrangements involve a firm selling an asset it owns and then leasing it back from the buyer.
Leveraged leases involve a third-party lender partially financing the purchase of an asset to be leased. Specialized service leases involve the lessee availing specialized services of the lessor for maintenance of the asset leased.
Let’s know them in detail with examples:
There are various types of leases, and the two most common ones are operating leases and financing leases (also known as capital leases). Let’s take a closer look at each type:
Operating Lease
This is a lease agreement that permits the use of an asset without transferring ownership rights to the lessee. In this type of lease, the lessor is responsible for maintaining the asset and bearing any risks associated with ownership. Such as depreciation, obsolescence, and maintenance costs.
The lessee pays rental payments and has the right to use the asset for a specified period of time. Operating leases are commonly used for assets that have a short useful life or are rapidly changing in terms of technology, such as office equipment or computer hardware.
For example, a company may lease a printer for its office on an operating lease. The lessor retains ownership of the printer. But the lessee has the right to use it for a specified period, such as three years. The lessee pays a monthly rental payment to the lessor, and the lessor. Both is responsible for any repairs or maintenance needed during the lease term.
Financing Lease (Capital Lease)
This is a lease arrangement that permits the lessee to utilize an item while transferring ownership rights at the lease’s conclusion. The lessee is responsible for the asset’s upkeep and risks. Such as depreciation, obsolescence, and maintenance costs, under this form of lease.
The lessee makes regular payments, which typically include interest and principal. To the lessor until the end of the lease term when ownership of the asset transfers to the lessee.
For example, a company may lease a truck for its transportation needs on a financing lease. The lessee is responsible for maintaining the truck and bearing any risks associated with ownership, such as repairs and maintenance costs. The lessee makes regular payments to the lessor, which include interest and principal, until the end of the lease term, at which point ownership of the truck transfers to the lessee.
Other types of leases include Sale and Lease-Back, Sales Aid Leases, and Specialized Service Leases.
Sale and Lease-Back
This is a type of lease where the lessor sells an asset to the lessee and then leases it back from the lessee for a specific period. This type of lease can provide the lessor with immediate cash while allowing the lessee to use the asset without incurring the full cost of ownership.
For example, a company may sell its factory to a lessor and then lease it back to use as its manufacturing facility. The company gets immediate cash from the sale, and the lessor can lease the factory to the company for a specified period.
Sales Aid Lease
This type of lease is used by manufacturers to help promote the sale of their products. In this type of lease, the lessor provides financing to the lessee to purchase the manufacturer’s product, and the lease payments cover the cost of the product and the financing charges.
An automobile manufacturer, for example, may offer its customers a sales assistance lease, in which the lessee can finance the purchase of a car through a lease arrangement with the manufacturer.
Specialized Service Lease
This type of lease is used for assets that require specialized maintenance and services. In this type of lease, the lessor is responsible for providing specialize maintenance and services, such as training and technical support.
Examples of other types of leases include absolute net leases, triple net leases, modified gross leases, and full-service leases.
Advantages of leasing
Advantages of leasing include cost savings, access to assets, flexibility, and tax benefits. Leasing can provide greater flexibility to users who may need to contract, as there is no ownership risk and it allows companies to upgrade assets, like equipment, which reduces the risk of obsolescence. In a lease, one party obtains the right to use an asset legally owned by another party for a period.
- Leasing equipment provides 100% financing, which can be conserved.
- Leasing equipment also allows for capital to be saved since the equipment can be replaced when it expires.
- Leasing equipment is more predictable than buying because the payments are fixed and known in advance.
- Leasing also provides a lot of flexibility in that the equipment can be replaced at the end of the lease with updated equipment.
- Leasing is a preferred solution to resolve fixed asset requirements vs. purchasing the asset.
- It is essential for the owner of the capital to understand whether leasing would yield better returns on capital or not.
- There are four likely outcomes following the termination of a lease agreement.
- Lease finance is appropriate for an individual or business which cannot raise money through other sources of finance like debt or term loans because of the lack of funds.
- The business or lessee cannot even arrange the down payment money to raise debt.
- The lease works best for him.
- But, the lessor, who wants to invest his money efficiently, becomes the financier for the lessee and earns the interest.
Disadvantages of Leasing
Disadvantages of leasing include a long-term commitment, no ownership rights, higher costs over time, and penalties for early termination.
Leasing is a popular financing option for both organizations and people, but it’s crucial to weigh the benefits and drawbacks before making a decision.
One of the biggest disadvantages of leasing is the long-term commitment. When you sign a lease, you agree to make regular payments for a set length of time. It could be monthly or yearly. This lack of flexibility can be a disadvantage for people who desire more freedom to modify their assets.
Another downside of leasing is that you do not have ownership of the asset. This means you can’t change the thing. And you cannot sell it or use it as related to a loan.
Leasing can potentially result in increased long-term expenditures. While the initial lease payments may be less than the cost of buying the asset outright, you may end up paying more in the long term due to interest and other costs.
Furthermore, if you decide to break the lease early, you may be liable to penalties and fees, which can be rather expensive. This lack of adaptability might be a significant disadvantage for individuals who need to adjust their assets or company plans.
Finally, leasing can also result in a loss of incentives to take ownership of the asset, as well as the potential loss of any salvage value of the asset.
While leasing may be a realistic choice for some, it is critical to carefully assess the benefits and drawbacks before making a decision.
Quiz
[quiz-cat id=”4431″]
Was this helpful?
0 / 0