Definition
A product can be defined as anything that can be presented to the market for consideration, acquisition, usage, or consumption, which may fulfil a desire or requirement.
These definitions are more comprehensive, as illustrated in an exhibit, and provide a better understanding of the nature and purpose of products.
In contemporary marketing, a product is defined as a combination of tangible and intangible attributes that satisfy consumers’ wants or needs. It can be anything that can be offered to the market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption.
The functional aspects of a product may be of minor importance as compared to intangible attributes such as brand name, style, and social-symbolic meanings that consumers attach to a product.
Marketers need to consider these intangibles when marketing a product, especially for products used in public or social settings. Today, a product does not have to be a physical entity, services are also considered products. Consumers do not buy products, they buy satisfaction.
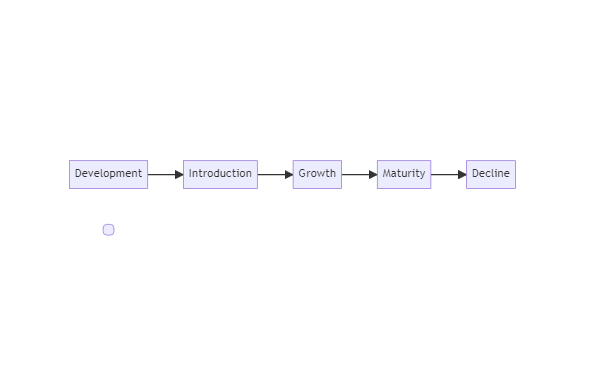
The product life cycle refers to the different stages that a product goes through, from its introduction to the market to its eventual decline.
Types of Products
There are different types of products that companies can offer, including:
Tangible Products
Tangible products are physical objects that can be seen, touched, and experienced. Examples of tangible products include clothing, electronics, and toys.
Intangible Products
Intangible products are services or experiences that cannot be physically touched. Examples of intangible products include insurance, consulting services, and education.
Durable Products
Durable products are items that are designed to last for a long time. Examples of durable products include cars, appliances, and furniture.
Non-Durable Products
Non-durable products are items that are designed for one-time or short-term use. Examples of non-durable products include food, cleaning supplies, and personal care products.
Factors Influencing Product Success
There are several factors that can influence the success of a product, including:
- Market demand
- Competition
- Quality
- Price
- Promotion
- Distribution
Market demand: This refers to the willingness and ability of customers to buy a product. Market demand is a critical factor in determining the success of a product as it indicates the potential for sales and revenue.
Competition: This refers to other products and businesses offering similar products. Competition can impact the success of a product by affecting its market demand, pricing, and promotion efforts.
Quality: This refers to the standard and features of the product. A product with high quality is more likely to succeed in the market as customers are more likely to buy and recommend it to others.
Price: This refers to the cost of the product in comparison to others. Price is an important factor as it affects the affordability and value of the product to customers.
Promotion: This refers to the marketing and advertising efforts to increase awareness and interest in the product. Effective promotion can increase market demand and improve brand recognition, leading to increased success for the product.
Distribution: This refers to the availability and accessibility of the product to customers. A product’s distribution network affects its reach and accessibility, which in turn can impact its success.
Was this helpful?
0 / 0